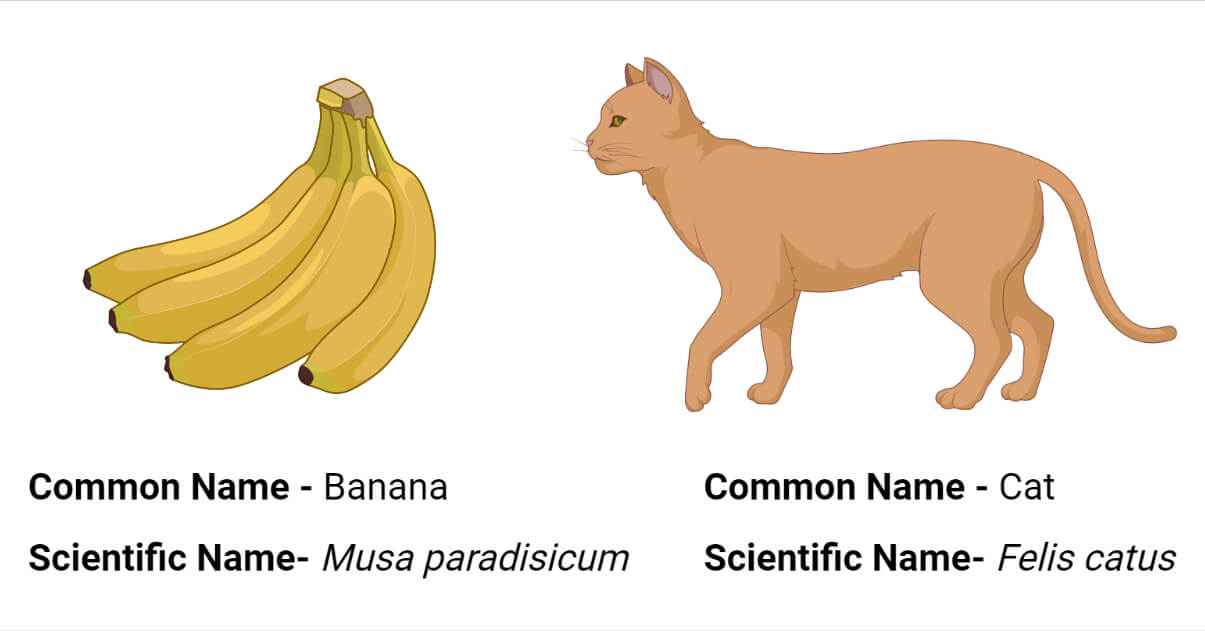

Scientific nomenclature refers to various names according to a specific field of study. Usually, animals & plants are identified by common and scientific names.

Table of Contents
Interesting Science Videos
The following codes are used today:
It is the set of guidelines and recommendations that control the scientific naming of all organisms previously categorized as algae, fungi, or plants, whether they are fossil or non-fossil. This includes blue-green algae (Cyanobacteria), chytrids, oomycetes, slime molds, and photosynthetic protists along with their taxonomically related non-photosynthetic groups (but excluding Microsporidia).
The ICZN produces and disseminates information on how to correctly use the scientific names of animals, serving as an advisor and arbiter for the zoological community.
The International Code of Zoological Nomenclature, a set of guidelines for animal naming and the solution of nomenclatural issues, is established by the ICZN.
Prokaryotes, comprising eubacteria and archaebacteria or archaea, are classified according to the International Committee on Systematics of Prokaryotes (ICSP) and the International Code of Nomenclature of Bacteria.
The ICNCP is a manual for naming cultigens, or plants whose origin or selection is primarily attributable to deliberate human action.
Grexes, Groupings (cultivar groups), and Cultigens all fall under the scope of the ICNCP.
It includes all species that are typically classified as plants, including fungi and alga.
Taxa that are given names under the ICNCP will also be included in the taxa named under the International Code of Nomenclature for Algae, Fungi, and Plants.
It consists of definitions, principles, articles, recommendations, and a guide to the correct formation of names of syntax based on the names of plant species.
ICTV is a committee of the Virology Division of the International Union of Microbiological Societies.
The Statutes define the objectives of the ICTV are:
The levels from highest to lowest classification are as follows:
In hand-written texts, it can be underlined instead, however when using a Word processor, there is no justification for not italicizing.
Example: Bos taurus, not Bos taurus.
Example: Antibiotic resistance observed in Escherchia coli.
Example: Juniperus virginiana, not Juniperus Virginia.
The abbreviation “spp.” is similarly used to indicate a group of unknown species.
The term “sp. novo” is used to indicate a species that is being described for the first time.
The first initial and a period can be used to shorten the genus in subsequent uses.
Example: “Escherichia coli is a lactose fermenting Gram-negative bacteria. The cases of antibiotic resistance E. coli has been reported frequently.”
Example: Staphylococcus aureus and Streptococcus pyogenes instead of S. aureus and S. pyogenes.
Example: Tribolium confusum or T. confusum but never just confusum.
Example: There are many species of Drosophila that are affected by exposure to alcohol.
Example: Pan troglodytes (chimpanzee)
Example: Juncus inflexus L..
Carolus Linnaeus, an eminent scientist whose name was Latinized, was abbreviated to “L”
The name of the pants at the end generally ends with the plural adjective which in Latin is “aceae”. The adjective used generally describes the genus or the family characteristics to which the particular plant belongs.
Some of the Scientific names of common plants are as given below:
| Common Name | Scientific Name |
| Apple | Pyrus malus |
| Bamboo | Bamboosa aridinarifolia |
| Brinjal | Solanum melongena |
| Banana | Musa × paradisiaca |
| Black Gram | Vigna mungo |
| Banyan | Ficus benghalensis |
| Barley | Hordeum vulgare |
The system of naming the animals is similar to that of the plant’s naming system. During the nomenclature of the animals, the genus comes first and then is followed by the species.
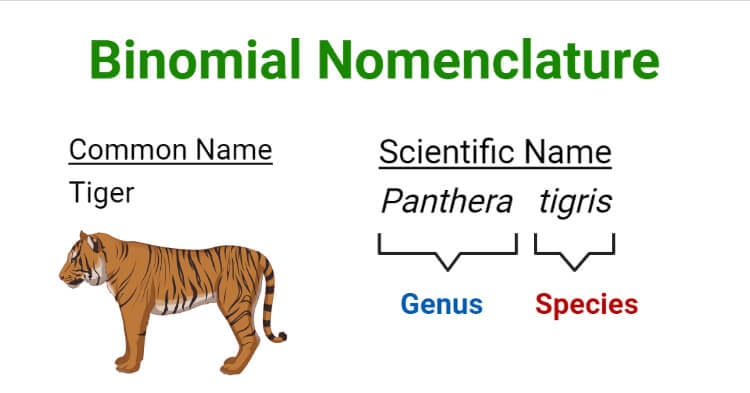
Some of the scientific names of animals are as follows:
| Common Name | Scientific Name |
| Dog | Canis familiaris |
| Cat | Felis catus |
| Horse | Equus ferus caballus |
| Sheep | Ovis aries |
| Domestic Pig | Sus scrofa domesticus |
| Wild Goat | Capra aegagrus hircus |
| Asian Elephant | Elephas maximus |
Phylogenetic and evolutionary research has helped to connect the relationship of extinct animals with the surviving organisms, and its nomenclature is similar to the other organisms.
Some of the lists of the scientific names of extinct animals are as follows:
| Common Name | Scientific Name |
| Passenger pigeon | Ectopistes migratorius |
| Tasmanian tiger | Thylacinus cynocephalus |
| Moa | Dinornithiformes |
| T-Rex | Tyrannosaurus rex |
| Dolphin | Lipotes vexillifer |
Common names, in contrast to scientific names, are not exclusive.
Therefore, using common names can cause misunderstandings regarding the animal being referred to and its relationships to other animals.
Although they are all called badgers and they are all members of the same mammalian family, they are not each other’s closest relatives. There are various animals worldwide that are superficially similar.
Eliminates confusion between nationalities that may have different common names for organisms by assigning them a universal name that acts as a code.
About Author